

Dental infections are commonly caused by bacteria that invade dental pulp and spread to surrounding tissues. If dental infections aren’t treated and continue to spread, a pus-filled abscess can form. A tooth abscess can affect different parts of a tooth, as well as gum tissue and bone. Pus in a dental abscess is made of dead tissue, white blood cells and bacteria. Typically, the onset of a dental abscess is slow and may take several months to produce obvious symptoms. But when an acute periapical abscess (one that forms in the tissues surrounding the apex of the root of a tooth) develops, it’s common to experience a more rapid onset of well-localized pain.
Typically, the onset of a dental abscess is slow and may take several months to produce obvious symptoms.

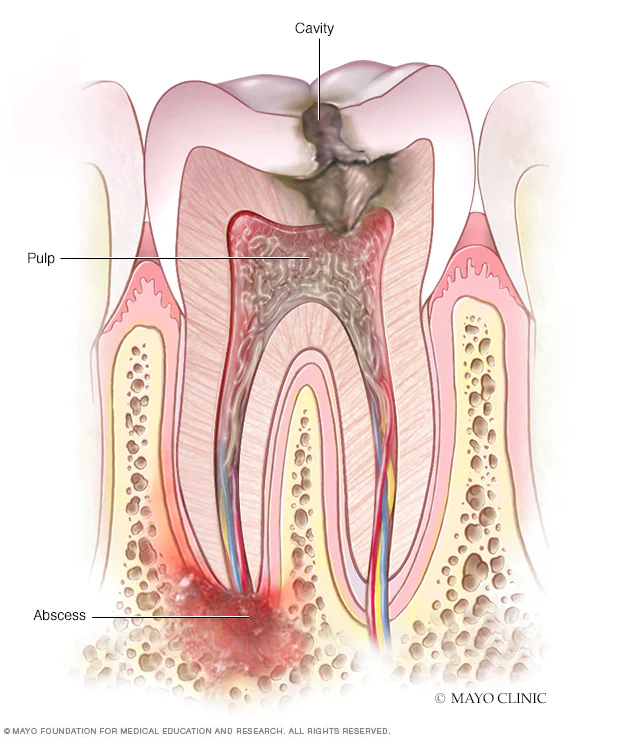

A periodontal abscess causes localized accumulation of pus within the gingival wall of a periodontal pocket. A periodontal abscess looks like a small red ball pushing out of the swollen gum tissue. This type of abscess, which can occur during gum disease treatment or as a result of untreated periodontal disease, is more common in patients with previous periodontal pockets. Abscesses unrelated to gum disease are caused by the impaction of foreign objects (e.g., a piece of dental floss) or abnormalities of your root anatomy.

Although a dentist can help diagnose an abscess, endodontists specialize in treating infected teeth and pulp, and they have advanced training and technology to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. At Advanced Endodontics of New York, our endodontists have extensive expertise in treating abscessed teeth in New York, NY. Prompt intervention for a dental abscess is essential and our practice is equipped to deal with endodontic emergencies.
Management of dental abscesses includes incision and drainage, root canal therapy, apicoectomy and tooth extraction. In some patients, antibiotics may be prescribed.
During an incision and drainage, the area around the abscess is numbed with local anesthesia. Then your gums are carefully incised and we drill into your tooth using specialized tools. Once the abscess is accessed, the infected matter is removed and the pus is drained. Next, the area is irrigated with a sterile saline solution to remove any residual bacteria or debris. After we’re certain all the infected matter and pus have been removed, we close the incision with a few sutures and/or fill the infected tooth. In some cases, a small rubber drain is placed in the abscess site to drain any pus that the body may continue to produce. The drain is typically removed within three days, after which we apply sutures or fill the impacted tooth.
During a root canal, the infected tooth roots are accessed through the crown of your tooth, then the canal is thoroughly cleaned, shaped, filled and sealed. A restorative crown is required to protect the weakened tooth and fully restore its function.
An apicoectomy involves making an incision in the gum tissue to expose the bone and surrounding inflamed tissue. Then the damaged tissue is removed along with the end of the apex. A root-end filling is placed to prevent reinfection of the root, and the gum tissue is sutured. The bone naturally heals around the root over a period of months, thereby restoring full function to the tooth.
I understand the information disclosed in this form may be subject to re-disclosure and may no longer be protected by HIPAA privacy regulations and the HITECH Act.
